Will My Body Protect My Baby if I'm Anemic
Anemia occurs in up to one third of women during the 3rd trimester. The virtually common causes of anemia are
If women have a hereditary anemia (such as sickle prison cell disease Sickle Cell Disease Sickle cell disease is an inherited genetic aberration of hemoglobin (the oxygen-carrying protein institute in red claret cells) characterized by sickle (crescent)-shaped scarlet blood cells and chronic... read more 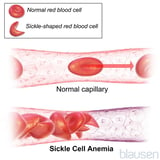 , hemoglobin S-C disease Hemoglobin C, S-C, and E Diseases Hemoglobin C, Southward-C, and E diseases are inherited weather condition characterized by gene mutations that bear upon the hemoglobin (the protein that carries oxygen) in red claret cells, causing the cells... read more , or some thalassemias Thalassemias Thalassemias are a group of inherited disorders resulting from an imbalance in the production of i of the iv chains of amino acids that make up hemoglobin (the oxygen-conveying protein found... read more than ), the risk of problems is increased during pregnancy. If women are at increased gamble of having any of these disorders because of race, indigenous groundwork, or family history, claret tests to check for the disorders Genetic Screening Genetic screening is used to determine whether a couple is at increased take chances of having a baby with a hereditary genetic disorder. Hereditary genetic disorders are disorders of chromosomes or... read more are routinely washed before delivery. Chorionic villus sampling Chorionic Villus Sampling Prenatal diagnostic testing involves testing the fetus before birth (prenatally) to determine whether the fetus has certain abnormalities, including certain hereditary or spontaneous genetic... read more or amniocentesis Amniocentesis Prenatal diagnostic testing involves testing the fetus before nativity (prenatally) to determine whether the fetus has certain abnormalities, including certain hereditary or spontaneous genetic... read more may be washed to cheque for these disorders in the fetus.
, hemoglobin S-C disease Hemoglobin C, S-C, and E Diseases Hemoglobin C, Southward-C, and E diseases are inherited weather condition characterized by gene mutations that bear upon the hemoglobin (the protein that carries oxygen) in red claret cells, causing the cells... read more , or some thalassemias Thalassemias Thalassemias are a group of inherited disorders resulting from an imbalance in the production of i of the iv chains of amino acids that make up hemoglobin (the oxygen-conveying protein found... read more than ), the risk of problems is increased during pregnancy. If women are at increased gamble of having any of these disorders because of race, indigenous groundwork, or family history, claret tests to check for the disorders Genetic Screening Genetic screening is used to determine whether a couple is at increased take chances of having a baby with a hereditary genetic disorder. Hereditary genetic disorders are disorders of chromosomes or... read more are routinely washed before delivery. Chorionic villus sampling Chorionic Villus Sampling Prenatal diagnostic testing involves testing the fetus before birth (prenatally) to determine whether the fetus has certain abnormalities, including certain hereditary or spontaneous genetic... read more or amniocentesis Amniocentesis Prenatal diagnostic testing involves testing the fetus before nativity (prenatally) to determine whether the fetus has certain abnormalities, including certain hereditary or spontaneous genetic... read more may be washed to cheque for these disorders in the fetus.
When anemia develops, the claret cannot carry as much oxygen as it normally does. At commencement, anemia causes no symptoms or only vague symptoms, such as fatigue, weakness, and light-headedness. Affected women may look pale. If anemia is astringent, the pulse may exist rapid and weak, women may faint, and blood pressure may exist low.
If anemia persists, the following may event:
-
The fetus may not receive enough oxygen, which is needed for normal growth and evolution, especially of the brain.
-
Pregnant women may become excessively tired and curt of breath.
-
After delivery, the take a chance of infection in the woman is increased.
The haemorrhage that unremarkably occurs during labor and delivery can dangerously worsen anemia in these women.
-
Blood tests
Anemia is normally detected when doctors exercise a routine complete blood count at the offset exam subsequently pregnancy is confirmed.
-
Treatment of the anemia
-
For severe symptoms or sure issues in the fetus, transfusions
Measures to correct anemia during pregnancy depend on the cause (come across below).
Whether claret transfusions are needed depends on whether the following occur:
-
Symptoms, such as lite-headedness, weakness, and fatigue, are astringent.
-
Anemia affects animate or the heart rate.
-
The middle rate pattern in the fetus is abnormal.
-
Not consuming enough iron in the diet (especially in adolescent girls)
-
Menstruating
-
Having had a previous pregnancy
Women normally and regularly lose iron every month during catamenia. The amount of iron lost during menstruum is nigh the same as the amount women normally eat each month. Thus, women cannot store much iron.
Claret tests can ostend the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia or folate deficiency anemia.
Anemia can unremarkably exist prevented or treated by taking iron and folate supplements during pregnancy. If a pregnant woman has fe deficiency, the newborn is usually given iron supplements. Taking folate supplements before becoming meaning and during pregnancy reduces the risk of the baby having a neural tube defect.
A sudden, severe attack of pain, called sickle cell crisis, may occur during pregnancy as at any other fourth dimension. The more severe that sickle cell disease is earlier pregnancy, the college the risk of health problems for pregnant women and the fetus, and the higher the risk of death for the fetus during pregnancy. Sickle cell anemia almost ever worsens every bit pregnancy progresses.
If given regular claret transfusions, women with sickle cell disease are less likely to have sickle cell crises, but they become more than likely to reject the transfused claret. This condition, called alloimmunization, can be life threatening. As well, transfusions to significant women do non reduce risks for the fetus. Thus, transfusions are used only if ane of the following occurs:
-
The anemia causes symptoms, centre failure, or a astringent bacterial infection.
-
Serious bug, such equally haemorrhage or an infection of the blood (sepsis), develop during labor and delivery.
If a sickle cell crisis occurs, women are treated every bit they would exist if they were not pregnant. They are hospitalized and given fluids intravenously, oxygen, and drugs to relieve pain. If the anemia is severe, they are given a claret transfusion.
CLICK HERE FOR THE Professional person VERSION

© 2022 Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, United states
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-issues/pregnancy-complicated-by-disease/anemia-during-pregnancy
0 Response to "Will My Body Protect My Baby if I'm Anemic"
Post a Comment